How Health Insurance Works In The United States
Understanding How Health Insurance Works in the United States can often feel like navigating a complex maze. With a system that has evolved over decades and encompasses various types of plans, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of health insurance to make informed decisions. This overview aims to clarify how different plans operate, the role of insurance companies, and the costs associated with healthcare, ensuring that you are well-equipped to handle your health insurance needs.
From the foundational concepts to the practicalities of enrollment and the challenges individuals face, this exploration sheds light on the intricacies of health insurance, providing valuable insights into a system that significantly impacts everyday life.
Overview of Health Insurance in the United States
Health insurance in the United States serves as a critical safety net that helps individuals manage the costs associated with medical care. It enables access to necessary health services while protecting against the financial risks posed by unexpected health issues. As a complex system influenced by various factors, health insurance varies widely and continues to evolve with societal needs and legislative changes.The concept of health insurance has evolved significantly over the years in the U.S., with its roots tracing back to the early 20th century when hospitals began offering pre-paid services.
Initially, these arrangements were limited, but the post-World War II era saw a dramatic increase in employer-sponsored health plans, largely due to wage controls and the need to attract workers. The introduction of Medicare and Medicaid in the 1960s marked a pivotal moment in U.S. healthcare, extending access to the elderly and low-income populations. Over the decades, the landscape has changed further, with the Affordable Care Act of 2010 expanding coverage options and emphasizing preventive care.
Today, the American health insurance market is characterized by a variety of plans that cater to different needs and preferences.
Major Types of Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the different types of health insurance plans is vital for making informed choices about coverage. Each plan has distinct features that cater to various healthcare needs, and they can be classified into several main categories:
- Employer-Sponsored Insurance: This type is provided by employers as part of employee benefits. It often covers a significant portion of premiums, making it a popular choice among workers.
- Individual Health Insurance: Individuals can purchase this type of insurance directly from insurance companies or through exchanges. It is suitable for those who are self-employed or do not have access to employer-sponsored plans.
- Government Programs: Programs like Medicare and Medicaid offer health coverage for specific groups, including seniors and low-income individuals. These programs ensure that vulnerable populations receive necessary medical care.
- Short-Term Health Insurance: Designed to provide temporary coverage during gaps in insurance, these plans are generally less comprehensive but can help manage costs in the short term.
- Catastrophic Health Insurance: This type of plan is aimed at younger, healthier individuals and typically has lower premiums but higher deductibles. It provides coverage for severe illnesses or accidents.
The variety of health insurance plans available allows individuals to select the option that best meets their health care needs and financial situations. Understanding these options is essential for navigating the complexities of the U.S. healthcare system effectively.
How Health Insurance Works

Source: healthinsuranceproviders.com
Understanding how health insurance operates is vital for anyone navigating the U.S. healthcare system. Health insurance provides financial protection against high medical costs, and comprehending its mechanics can help individuals make informed decisions about their health coverage. This section explores the fundamental components of health insurance, including premiums, deductibles, and copayments, along with the role of insurance companies in the healthcare landscape.
Components of Health Insurance
Health insurance plans comprise several key components that affect how individuals pay for medical services. These elements include premiums, deductibles, and copayments, each playing a crucial role in how individuals manage their healthcare expenses.
- Premiums: This is the monthly fee that individuals or employers pay to maintain health insurance coverage. Premiums can vary significantly based on factors such as the type of plan, coverage level, and individual health needs.
- Deductibles: The deductible is the amount an insured person must pay for healthcare services before their insurance begins to cover costs. For example, if a plan has a $1,000 deductible, the insured must pay the first $1,000 of their medical expenses out of pocket before insurance kicks in.
- Copayments: A copayment, or copay, is a fixed amount that a policyholder pays for a specific service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription medication, usually at the time of service. Copayments can vary depending on the type of service received.
Role of Health Insurance Companies
Health insurance companies serve as intermediaries between patients and healthcare providers, facilitating the payment process for medical services. Their primary functions include:
- Risk Management: Insurance companies assess risk through underwriting processes, determining the premiums charged to policyholders based on their health status, age, and other factors.
- Claims Processing: When a policyholder receives medical services, the healthcare provider submits a claim to the insurance company. The insurer reviews the claim, determining the extent of coverage and any costs the policyholder is responsible for.
- Provider Networks: Many insurance plans include a network of healthcare providers. Insurers negotiate rates with these providers, enabling them to offer lower costs to policyholders who choose in-network services.
Filing a Claim and Receiving Benefits
Filing a claim is a crucial process in accessing health insurance benefits. This typically involves the following steps:
- The healthcare provider bills the insurance company directly for the services rendered to the patient.
- The insurance company reviews the claim against the policy terms and conditions to determine coverage eligibility.
- Once approved, the insurer pays the provider according to the agreed-upon rates, and the patient is billed for any remaining costs, such as deductibles or copayments.
Understanding these mechanics is essential for making the most out of your health insurance plan and effectively managing healthcare expenses.
Types of Health Insurance Plans

Source: conneticsusa.com
Health insurance plans in the United States come in various forms, each designed to meet different healthcare needs and preferences. Understanding the differences among these plans helps consumers make informed choices about their health coverage. This section explores the most common types of health insurance plans, including HMO, PPO, EPO, and POS, highlighting their unique features, advantages, and disadvantages.
Comparison of Health Insurance Plans
When considering health insurance, it’s essential to recognize the key distinctions between the various types of plans available. Below is a comparison of HMO, PPO, EPO, and POS plans, summarizing their core characteristics, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
| Plan Type | Network | Primary Care Physician (PCP) | Specialist Referrals | Out-of-Network Coverage | Premium Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | Restricted to network | Required | Required | No coverage except emergencies | Generally lower |
| PPO | Flexible network | No requirement | No requirement | Partial coverage available | Generally higher |
| EPO | Restricted to network | No requirement | No requirement | No coverage except emergencies | Generally moderate |
| POS | Flexible network | Required | Required | Partial coverage available | Generally moderate |
The following Artikels the advantages and disadvantages of each plan type:
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization)
-
Advantage: Typically lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
-
Disadvantage: Limited provider choice and no out-of-network coverage.
-
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization)
-
Advantage: Greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and specialists.
-
Disadvantage: Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
-
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization)
-
Advantage: No need for referrals, with lower costs than PPOs.
-
Disadvantage: No out-of-network coverage except for emergencies.
-
- POS (Point of Service)
-
Advantage: Combines features of HMO and PPO, offering flexibility while requiring a PCP.
-
Disadvantage: Higher costs for out-of-network services.
-
Government Programs and Regulations
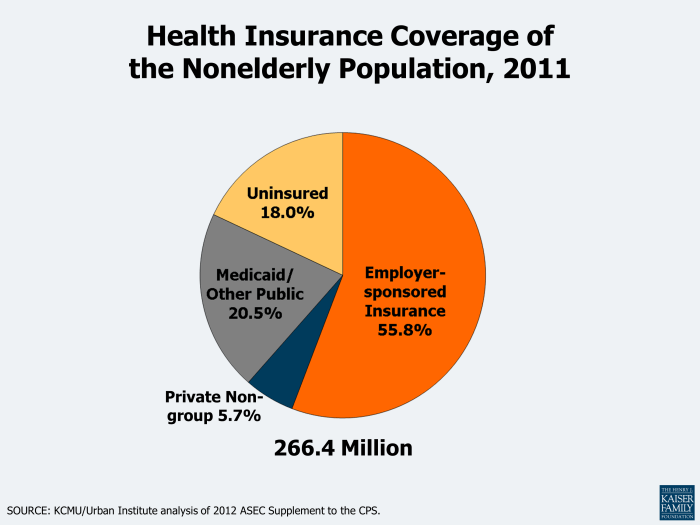
Source: kff.org
Government programs and regulations play a significant role in shaping the landscape of health insurance in the United States. They not only provide essential coverage for specific populations but also influence the overall accessibility and affordability of healthcare services. Understanding these programs and regulations is crucial for anyone navigating the U.S. healthcare system.The government offers various programs designed to assist those in need of health insurance, with Medicare and Medicaid being two of the most prominent.
Medicare caters primarily to individuals aged 65 and older, providing them with health coverage that includes hospital care, medical services, and prescription drugs. Medicaid, on the other hand, serves low-income individuals and families, ensuring access to necessary health services based on income eligibility. Both programs significantly increase access to necessary medical care for millions of Americans, helping to alleviate the financial burden of healthcare.
Impact of the Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), enacted in 2010, has had a transformative effect on health insurance coverage in the United States. It aimed to expand access to affordable health insurance and reduce the number of uninsured individuals. One of its key provisions was the establishment of health insurance marketplaces, allowing individuals to compare and purchase insurance plans. Additionally, the ACA mandated that insurance companies cover pre-existing conditions, meaning individuals could no longer be denied coverage based on their health status.Another significant impact of the ACA was the expansion of Medicaid eligibility in participating states, which enabled millions of low-income individuals to gain access to health care.
The ACA also introduced subsidies to help lower-income families afford insurance premiums, making healthcare economically accessible. Overall, the ACA has played a crucial role in reducing the uninsured rate and improving the overall health coverage landscape.
Key Regulations Governing Health Insurance
Several regulations govern health insurance in the U.S., each designed to protect consumers and ensure fair practices within the industry. Understanding these regulations is vital for consumers to navigate their health insurance options effectively. Here are some key regulations that shape health insurance in the U.S.:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): This law provides privacy protections for individuals’ health information and ensures that individuals can maintain their health insurance coverage when changing jobs.
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA): The ACA, as mentioned earlier, includes various provisions that prohibit discrimination based on pre-existing conditions and requires essential health benefits in insurance plans.
- Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP): This program provides health coverage to children in families with incomes too high to qualify for Medicaid but too low to afford private coverage.
- Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA): This legislation includes provisions that affect Medicare payment systems and the delivery of care, focusing on quality and value in healthcare services.
These regulations collectively aim to enhance consumer protections, improve access to healthcare services, and promote a fair and efficient health insurance market.
Costs and Financing of Health Insurance
Health insurance costs are essential to understand as they significantly impact individuals and families. The expenses associated with health insurance can vary widely based on several key factors, including the type of plan selected, the level of coverage, and personal health circumstances. Grasping these elements helps consumers make informed decisions regarding their health insurance options.Various factors directly influence the cost of health insurance premiums.
These include age, geographic location, tobacco use, individual and family health history, and the specific insurance provider. For instance, premiums tend to increase with age due to higher healthcare usage. Moreover, individuals living in areas with higher healthcare costs will often face higher premiums. Additionally, tobacco users may incur up to 50% higher premiums compared to non-tobacco users.
Out-of-Pocket Costs Variability
Out-of-pocket costs represent the expenses that insured individuals must pay before their insurance coverage kicks in. These can vary significantly between different health insurance plans. Understanding these costs is critical for budgeting and financial planning. Examples of common out-of-pocket costs include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Here are examples illustrating how out-of-pocket costs can differ among various plans:
- High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) usually have lower premiums but higher deductibles. For instance, a plan might have a deductible of $6,000, meaning the insured pays the first $6,000 of their medical bills before insurance starts covering costs.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) often have higher premiums but lower deductibles and copayments. A PPO may charge a $300 deductible and a 20% coinsurance for specialist visits, meaning if a visit costs $200, the insured would pay $40.
Potential Costs Associated with Different Health Insurance Options
A clear understanding of potential costs associated with different health insurance options is vital for making informed choices. The table below summarizes various health insurance types and their estimated costs.
| Health Insurance Type | Average Monthly Premium | Annual Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employer-Sponsored Plan | $500 | $1,500 | $6,000 |
| Individual Marketplace Plan | $600 | $3,000 | $8,000 |
| Medicaid | $0 | $0 | $2,000 |
| Medicare | $150 | $1,500 | $7,500 |
This table provides a snapshot of the average costs associated with different health insurance plans, illustrating how premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums can vary widely. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right plan based on individual financial situations and healthcare needs.
The Enrollment Process
The enrollment process for health insurance in the United States can seem overwhelming, but understanding the key steps can simplify it significantly. Whether you are enrolling for the first time or switching plans, knowing the timeline and requirements will help you make informed decisions.The enrollment process typically involves several key steps. First, individuals need to assess their health care needs and budget.
Next, they must gather necessary documents, such as income verification and personal identification. After this, they can explore the available health insurance plans during the enrollment period, ensuring they understand the coverage options, costs, and networks involved. Finally, applicants will complete their applications and make their premium payments to finalize their enrollment.
Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods
Understanding the different enrollment periods is crucial for ensuring that you have access to health insurance coverage when you need it. The Open Enrollment Period is a designated time each year when individuals can enroll in or change their health insurance plans without needing a qualifying event. This period usually lasts for a few weeks in the fall and is crucial for those who want to avoid gaps in coverage.Conversely, the Special Enrollment Period allows individuals to enroll in a health insurance plan outside the Open Enrollment timeframe due to specific qualifying events.
These events can include getting married, having a baby, losing other health coverage, or moving to a new area. The duration of these special periods is typically 60 days following the qualifying event.
Strategies for Selecting the Right Health Insurance Plan
Choosing the right health insurance plan requires a thorough understanding of personal health needs, financial situations, and plan options. Here are some strategies to consider while making this important decision:
1. Assess Your Health Care Needs
Consider your medical history, frequency of doctor visits, and any ongoing treatments. This will help you estimate the type and amount of coverage you’ll need.
2. Evaluate Costs
Look beyond just the premium. Understand the out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Aim to find a balance between premium and potential care costs.
3. Check Network Providers
Verify that your preferred doctors and hospitals are included in the insurance network. Out-of-network care can be significantly more expensive.
4. Review Benefits and Coverage
Different plans offer varying levels of coverage, including preventive care, specialist visits, and prescription medications. Ensure the plan covers services that are important for your health.
5. Consider Flexibility
Some plans offer more flexibility in choosing providers or obtaining referrals. If you value choice, look for plans that accommodate this preference.
6. Utilize Online Resources
Many websites provide comparison tools that allow you to review different plans side-by-side. Use these tools to identify which plan meets your needs best.By taking these steps, individuals can navigate the enrollment process with confidence and choose a health insurance plan that aligns with their unique requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
Navigating the world of health insurance can be a daunting task for many individuals. With the complexity of policies and the variety of options available, understanding what is covered and what is not can be overwhelming. Numerous challenges arise, from deciphering jargon to managing out-of-pocket costs, making it essential for consumers to equip themselves with the right knowledge and resources.One of the primary hurdles people face is comprehending the specific terms and conditions of their health insurance plans.
Coverage limits and exclusions can significantly impact the financial burden on individuals during medical care. It’s crucial to grasp these limitations to avoid unexpected bills that could arise from services that are not covered under a plan.
Understanding Coverage Limits and Exclusions
Health insurance plans often come with various coverage limits and exclusions that dictate what services are included or excluded from coverage. Being well-informed about these aspects is vital for effective decision-making regarding healthcare needs. Coverage limits refer to the maximum amount an insurance company will pay for specific services within a given timeframe, often referred to as the policy year.
For instance, a plan may cover up to $20,000 for surgeries but have no coverage for cosmetic procedures. Exclusions, on the other hand, are specific scenarios where the insurer will not provide any financial assistance. Common exclusions may include pre-existing conditions, certain experimental treatments, or alternative therapies.To help navigate the complexities of health insurance, consumers can benefit from a variety of resources that provide valuable information and guidance.
Below is a list of recommended resources to better understand health insurance options:
- The Healthcare.gov website offers comprehensive information on available health plans, enrollment periods, and eligibility for financial assistance.
- State insurance department websites provide localized resources, including consumer complaints, plan comparisons, and advocacy guidance.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) offers tools to help consumers understand their rights and responsibilities regarding health insurance.
- Health insurance brokers can provide personalized guidance and support in choosing the right plan based on individual needs and circumstances.
- Nonprofit organizations such as Families USA and the Patient Advocate Foundation offer educational materials and assistance for navigating health insurance and healthcare services.
“Understanding your health insurance plan is the first step towards making informed healthcare decisions.”
The Future of Health Insurance
The landscape of health insurance in the United States is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and shifting consumer expectations. Emerging trends such as telemedicine and value-based care are reshaping the way health services are delivered and reimbursed. As these changes take root, they are likely to redefine the relationship between patients, providers, and insurers.Technological advancements are set to significantly influence health insurance models, making them more efficient and patient-centered.
The integration of artificial intelligence, mobile health applications, and data analytics will allow insurers to better assess risk, streamline claims processing, and personalize health plans. This shift towards a more data-driven approach not only enhances operational efficiencies but also empowers consumers to take charge of their health.
Emerging Trends in Health Insurance
Several notable trends are emerging in the health insurance sector, reflecting a shift towards innovative care delivery models.
- Telemedicine: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, enabling patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely. This trend is likely to continue, as it offers convenience and enhanced access to care, particularly for those in rural areas.
- Value-Based Care: Transitioning from fee-for-service to value-based care models focuses on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services provided. Insurers are incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality care, which improves health outcomes and reduces costs.
- Personalized Health Plans: With advancements in genomics and personalized medicine, health insurers are beginning to offer tailored plans that reflect individual health needs and preferences. This approach enhances patient engagement and satisfaction.
- Health Technology Integration: The use of health tech tools, such as wearable devices and mobile health apps, is on the rise. These technologies provide real-time health data, enabling insurers to monitor patients’ health and offer proactive care interventions.
Impact of Technological Advancements
The integration of emerging technologies is poised to reshape health insurance models significantly. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving efficiencies in claims processing and risk assessment.
“AI has the potential to reduce administrative costs by automating mundane tasks, allowing insurers to focus on enhancing customer service and care quality.”
The use of predictive analytics will enable insurers to identify high-risk patients and intervene early, potentially preventing more serious health issues down the line. Additionally, telehealth platforms can utilize data analytics to track patient outcomes and satisfaction, helping insurers refine their offerings.
Predictions for the Evolution of Health Insurance
Looking ahead, several predictions can be made regarding the future of health insurance in the United States.
- Increased consumer involvement in health insurance choices, leading to more personalized and transparent insurance offerings.
- Widespread adoption of value-based care, resulting in improved health outcomes and a reduction in overall healthcare spending.
- Greater collaboration between insurers and technology companies to develop innovative solutions that enhance patient care.
- Expanding regulatory frameworks that support the integration of new technologies while ensuring consumer protections and data privacy.
As these trends continue to unfold, the health insurance industry will likely become more adaptive and responsive to the changing needs of consumers, ultimately leading to a more efficient and effective healthcare system.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, navigating the world of health insurance in the United States may seem daunting, but understanding its core components can empower you to make better choices. With knowledge of various plans, costs, and enrollment processes, you can confidently select coverage that aligns with your needs. As the landscape of health insurance continues to evolve, staying informed will help you adapt to changes and ensure you have the best care possible.
FAQ
What is the difference between HMO and PPO plans?
HMO plans require members to choose a primary care doctor and get referrals for specialists, while PPO plans offer more flexibility to see any doctor without a referral.
Can I change my health insurance plan at any time?
Generally, you can only change your health insurance during open enrollment periods or qualifying life events, such as marriage or loss of coverage.
What is a deductible in health insurance?
A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket for healthcare services before your health insurance starts to pay.
How does the Affordable Care Act affect me?
The Affordable Care Act expanded access to health insurance, created regulations to protect consumers, and provided subsidies to help lower-income individuals afford coverage.
What should I consider when choosing a health insurance plan?
Consider factors like premiums, deductibles, network of providers, coverage options, and out-of-pocket maximums when selecting a plan.